Windows Hosts File Location and How-To Edit Hosts File in Windows 11
In the Windows operating system, the hosts file is a plain text file that can be used to map hostnames to IP addresses. The location of the hosts file is C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc.
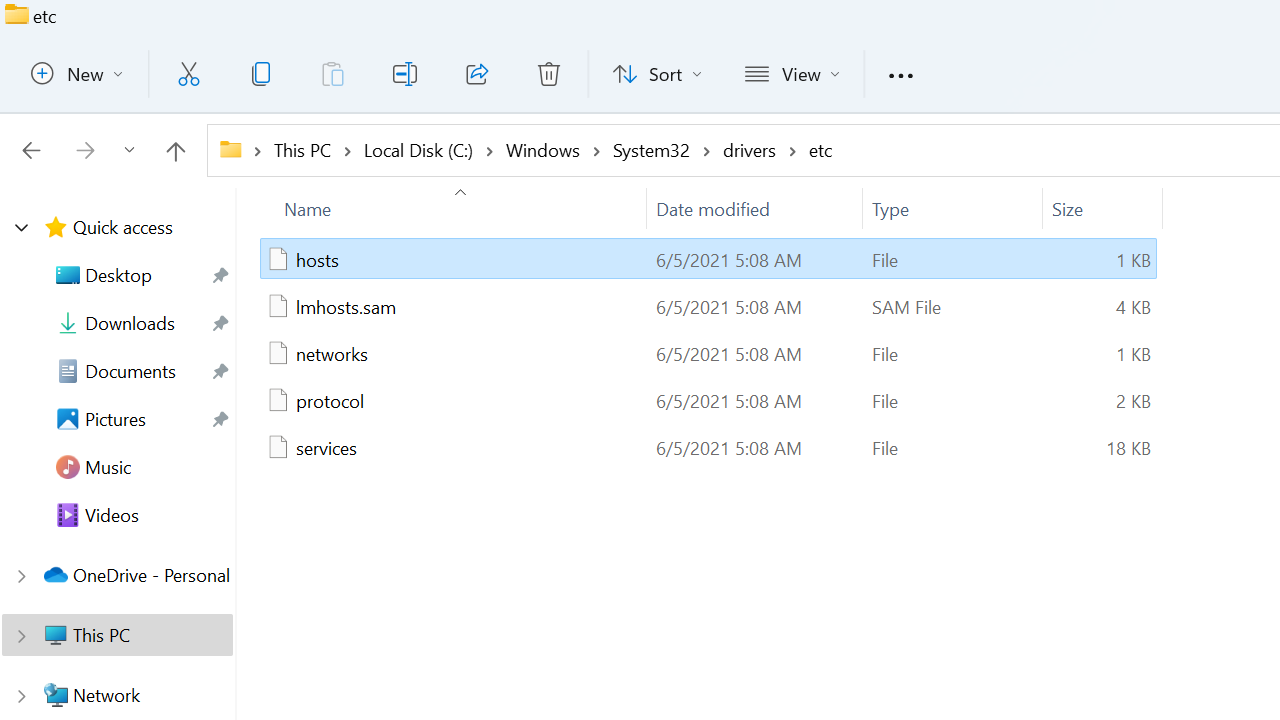
The following screenshot shows the default hosts file of Windows 11:
- The hosts file is a plain text file and has no filename extension.
- You can use File Explorer to navigate to the hosts file location.
- To edit this file, you need to open the editor as an administrator.
- The hosts file works the same way on all Windows Operating systems (Windows 10, 11, Windows Server, etc.).
Open Hosts File for Edit
You can edit the hosts in any text editor, such as notepad. The important point is that you need to open the notepad as administrator. There are a couple of ways we can do this.
The easiest way is to use the command prompt. Right-click the Start button and choose Window Terminal (Admin) from the menu. It is PowerShell (Admin) if you are on Windows 10.
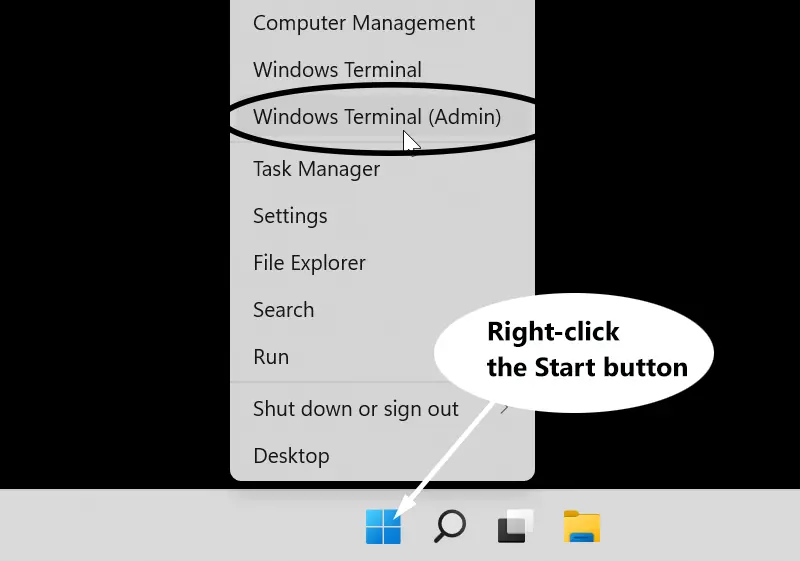
Next, execute the following command in the command prompt:
notepad C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hostsThe above command will open the hosts file for editing. It is as simple as that.
Map IP Addresses to Domain Names
In the hosts file, we map IP addresses to hostnames using the following format:
ip_address domain_nameEach line consists of an IP address followed by white-space(s) followed by hostname(s).
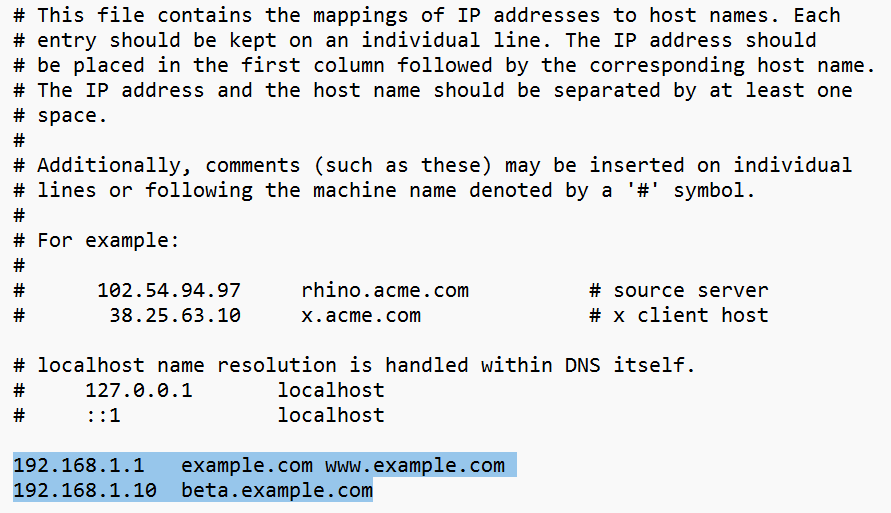
Before DNS, the hosts file was used (and still does) to map IP addresses to friendly names. Windows still uses it before querying a name server.
However, you should not manually edit the hosts file except for troubleshooting and testing.